How to Estimate Flooring Area and Cost
-
Identify the Shape of the Flooring Area and Choose the Appropriate Calculator
Begin by determining the shape of the area you need to cover with flooring. Common shapes include rectangles, squares, and irregular shapes. For rectangles and squares, you can use a simple length-by-width formula to calculate the area. For irregular shapes, you may need to break the area down into smaller, more manageable shapes or use a specialized area calculator. There are various online tools and apps available that can assist you in calculating the area based on the specific shape of your room.
-
Determine the Size of the Flooring Material
Next, you need to know the size of the individual flooring units, such as the dimensions of each tile or the width and length of each plank of wooden flooring. This information is crucial for calculating how many units you will need to cover the entire area. Make sure to consider any patterns or layouts that may require additional cuts or pieces.
-
Account for Gaps Between Flooring Units
Flooring units, especially tiles and some types of wooden planks, are typically installed with small gaps or joints between them to allow for expansion and contraction due to temperature changes and moisture. The standard gap size is often around 0.125 inches (or 1/8th of an inch), but this can vary depending on the type of flooring and the manufacturer's recommendations. Factor these gaps into your calculations to ensure you have enough material to cover the entire area, including the spaces between the units.
-
Estimate Labor and Accessory Costs
Installing flooring involves more than just purchasing the material. You also need to consider the cost of labor, which can vary significantly depending on the type of flooring, the complexity of the installation, and the local market rates. Additionally, there may be accessories and supplies required, such as underlayment, adhesives, grout, trims, and thresholds. Research and obtain quotes from local flooring contractors or installers to get a more accurate estimate of these costs.
-
Calculate the Total Cost
Now, add up all the costs: the cost of the flooring material, the labor costs, and the cost of any accessories and supplies. This will give you the total estimated cost of your flooring project. It's a good idea to include a buffer or contingency amount in your budget to cover any unexpected expenses or overages that may arise during the installation process.
- Measure Twice, Cut Once: Always double-check your measurements to ensure accuracy before purchasing materials.
- Shop Around: Compare prices from different suppliers to find the best deal on flooring material.
- Consider Waste: Factor in a certain percentage of waste when calculating the amount of material needed, especially for irregular shapes or patterns that require cutting.
- Timing: Plan your project during off-peak seasons when contractors may be less busy and offer better rates.
How to calculate flooring area
Area = length × width
A = l × w
Triangle (Heron's Formula)
Note: Heron's formula is typically used when the lengths of all three sides are known. For simplicity, the formula for the area of a triangle with a base and height is also provided.
Heron's Formula:s = (a + b + c) / 2
Area = √(s × (s - a) × (s - b) × (s - c))
Base and Height Formula:
Area = (1/2) × base × height
A = 0.5 × b × h
Square Annulus (Ring-shaped Square)
Note: A square annulus is not a common term. It could refer to a ring-shaped area between two squares. For simplicity, the formula for the area of an annulus (ring-shaped area) with circular boundaries is provided.
Annulus (Circular Boundaries):Area = π × (R² - r²)
where R is the outer radius and r is the inner radius.
Note: For a square annulus (if such a term is intended to describe a ring-shaped area between two squares), you would need to calculate the areas of the two squares and then subtract the smaller square's area from the larger square's area.
Circle
A = π × r²
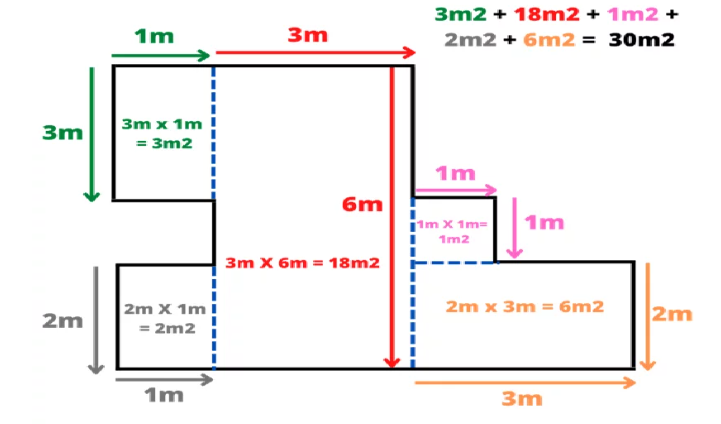
How to Measure an Irregular Room
Measuring an irregular room can be a bit tricky. Many areas are not square. You might have closets, bulges, or even fixed furniture like kitchen peninsulas that divide the space or make measuring more challenging.
However, the basic principles for measuring remain the same; you just need to take more measurements.
The first step is to divide the room into multiple square-like areas. Break down complex areas or corners into different sections that can be measured separately from the rest of the room.
When the room is divided into several imaginary square-like areas, use the method described above to calculate the area of each region.
The simplest approach might be to draw a simple floor outline of the room. Then, section off the room and identify the square portions.
Next, measure the length and width of each section and calculate its square footage as before. Write down the result for each section; you'll need it later.
Once you have calculated the square footage for each section, add them all together until you have accounted for all the floor space on your sketch.
Tips: Clearing your browsing data will remove bookmarks and usage history.